What is Text-to-SQL?
I recently stumbled across a tool called WrenAI that claims you can query any database using plain English. I was a little skeptical at first, but after burning through my free credits, I realized they weren’t bluffing. It felt kind of magical to ask questions in natural language and watch it generate relevant SQL and charts in real time.
As someone who works in data modeling and business intelligence, I know how critical a solid underlying model is. Your semantic and reporting layers are only as good as the foundation they sit on. So when a generative AI tool can consistently return useful SQL, readable tables, and insightful charts, you start to wonder if dashboards as we know them are about to be redefined.
What really caught my attention, though, was how tools like this could help democratize access to data. You don’t need to know SQL or even how to use a BI tool. This abstraction layer means non-technical users can get answers on their own, often in seconds. For data teams, that means fewer repetitive ad-hoc requests like “Can you pull sales by region?” or “Oh wait, can you add distribution channel to that?” and more time spent on better modeling and optimization work.
I was curious enough to dig into WrenAI GitHub repo to see how it all worked behind the scenes.
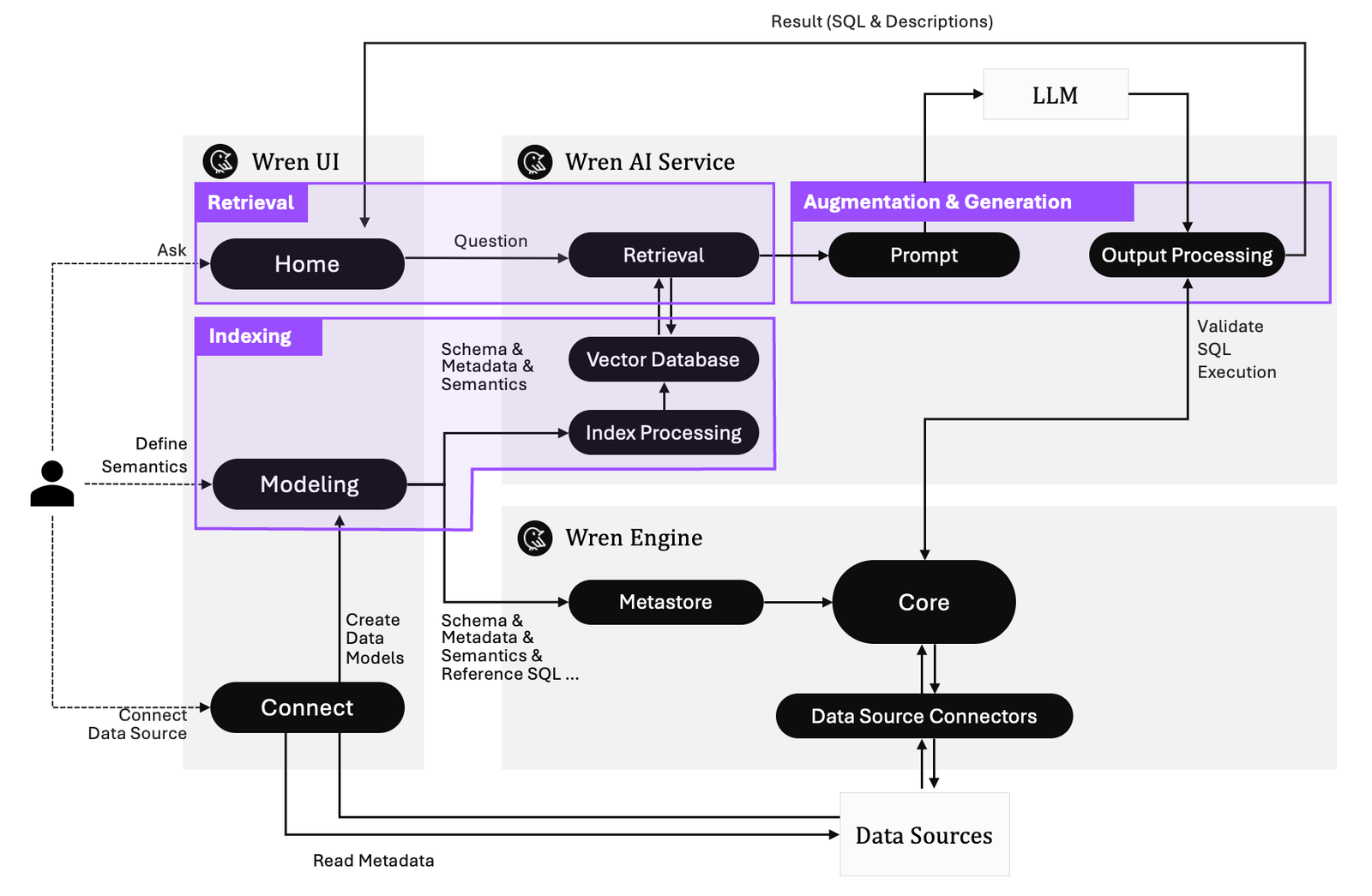
At first glance, it looks a bit overwhelming. But the point of this post, and the ones to follow, is to unpack that complexity and explore how these tools actually work under the hood.
Let’s start by breaking down the architecture diagram above.
1. Connect (Getting the Data In)
What it does:
This is where a Text-To-SQL system (e.g. WrenAI) connects to your actual data - databases, data warehouses, and more.
- Connect: Add a data source (like Synapse Analytics, Snowflake, Postgres, etc.)
- Reads Metadata: Grabs table names, column types, and other schema details
Think of it like introducing the Text-To-SQL system to your data for the first time.
2. Modeling (Defining the Semantics)
What it does:
Before WrenAI can do anything useful, you help it understand your data by defining semantics - descriptions, meanings, and relationships.
- You describe what fields mean (e.g.,
order_total= total sales). - It creates a semantic model to guide its understanding.
This is where you teach the system your organization’s vocabulary.
3. Indexing (Organizing the Knowledge)
What it does:
WrenAI processes your schema, metadata, and semantics, and stores them in a vector database for fast and relevant retrieval.
- Index Processing: Converts the model into vectorized data
- Vector Database: Makes that knowledge easily searchable
It’s like building a memory of your data that the AI can quickly reference.
4. Retrieval (Finding the Right Context)
What it does:
When a user asks a question, WrenAI looks through its vector memory to find the most relevant context - like tables, fields, and relationships.
- Retrieval Service: Matches the question to the right metadata
It’s like checking your notes before answering an exam question.
5. Prompting & Generation (Creating the SQL)
What it does:
Now WrenAI combines the user’s question with relevant context and forms a prompt for an LLM (like GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, you name it, the frontier models will always return better results) to generate SQL.
- Prompt: Merges question + metadata
- LLM: Generates the SQL query
- Output Processing: Validates the query to make sure it works
This is the smart part — translating natural language into working SQL.
6. Wren UI (The User Interface)
What it does:
This is what users see. You type your question into a chat-like interface, and WrenAI handles the rest.
- Sends your question to the backend
- Returns SQL results and visualizations
It’s the conversation window where data questions become answers.
7. Wren Engine (Query Execution Layer)
What it does:
Once the SQL is ready, it has to run somewhere. That’s the job of the Wren Engine.
- Core: Executes the SQL against the connected data source
- Metastore: Stores schema and semantic models for reuse
This is the engine room — quietly powering the results behind the scenes.
Summary in Plain English
You connect your data → define what it means → WrenAI processes and remembers it → when someone asks a question, it finds the right context → sends it to an AI to generate SQL → runs the SQL → and gives the user an answer.
Wrapping Up
Exploring WrenAI gave me a glimpse into what the future of analytics could look like: a world where anyone in a company can ask a question and get a useful answer instantly, without waiting days for a report or dashboard. Under the hood, it’s a blend of old-school data modeling, modern indexing, and generative AI — all working together.
What surprised me most is how much of this relies on concepts we already understand as data professionals: schemas, semantics, metadata, and SQL. The magic is in how they’re combined.
This is just the beginning. In upcoming posts, I’ll explore each piece in more depth, from building semantic models to how prompts are structured and validated, and share what I learn along the way. My goal is to better understand how to make data truly AI-ready, and I hope you’ll follow along. If you’re curious about this space or already exploring it yourself, let’s learn together.
Cheers,
Jorge Rocha
